Turbulent times in foreign trade
In 2024, the 8 Nordic countries had a combined import value of around 464 billion euro, and a combined export value of 540 billion. Sweden had the largest share of both imports and exports, while Denmark had the second largest import value and Norway the second largest export value. Intra-Nordic trade is substantial, it amounts to a fifth of all imports and exports, but the largest market is Europe with over half of all Nordic foreign trade. But times are turbulent - how has the Russian war on Ukraine effected trade flows, and how big is the trade with the US?
Foreign trade constitutes an important part of the economic activity in the Nordic countries. Nordic foreign trade in goods, measured as the average of imports and exports, amounts to more than one fourth of GDP in the Nordic countries. Denmark and Norway have had greater exports than imports every year since 2000, and Sweden only had four years where imports were greater than exports in the same period. In 2024, Denmark, Faroe Islands, Norway, and Sweden all had a surplus in their balance of trade.
Imports and exports in 2024
The trade between the Nordic countries is considerable. Of the combined value of all imports and exports in 2024, 21 and 19% respectively came from a Nordic country. Europe, excluding the Nordic countries, is the largest market, with a 55% share of imports and a 56% share of exports in 2024. Asia accounts for 14% of imports and 11% of exports, while South and North America has a combined share of 8% of imports and 10% of exports. [1] This distribution of flows in foreign trade has been relatively steady over the last 20 years.
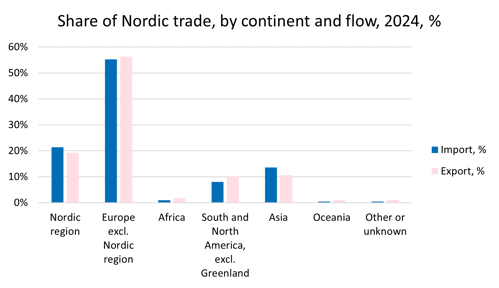
Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
Of the Nordic countries, Sweden has the largest import and export. Of the total value of all the Nordic imports, 38% was imported to Sweden. Of the total value of all the Nordic exports, 33% came from Sweden.
Denmark had the second largest import value, with 24%, while Norway accounted for 20%, Finland for 16% and Iceland for 2%. Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland had import values corresponding to less than 0.5% of the total Nordic import value.
Norway had the second largest export value, 29% of the total value of all exports to the Nordic region in 2024. Denmark came in third with 23%, Finland fourth with 13% and Iceland fifth with 1%. As with imports, Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland had export values corresponding to less than 0.5% of the total Nordic export value in 2024.
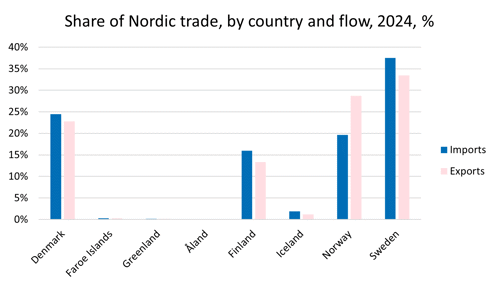
Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
The value of both imports and exports has grown over time, at a similar pace for all eight countries, meaning that the distribution of the combined Nordic foreign trade value has been quite steady over time. The exception is Norway, where the value of exports has fluctuated, especially in the last few years.
Trade with the Russian Federation
The Russian war on Ukraine has had far-reaching consequences regarding trade. Starting in 2022, heavy sanctions were imposed on the country and more have been added since.
For most Nordic countries, imports from Russia accounted for between 0 and 2% of the total value of imports between 2001 and 2021. Sweden had a slightly higher level during a part of the period, up towards 6%, but the big exception was Finland. Between 2002 and 2021, the value of Finnish imports from Russia varied between 10 and 18% of the total value of Finnish imports. In 2022 there was a drop down to 7% and in 2024 the share was 1%. Despite this decline, Finland however still had the highest share of Russian imports in 2024, all other Nordic countries had values below 0.5%.
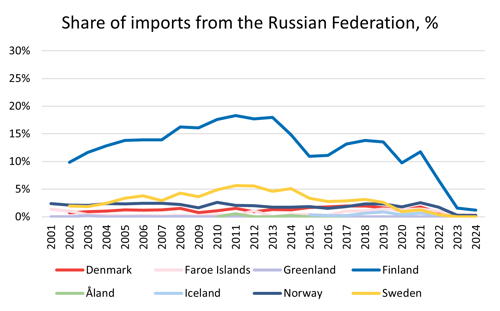
Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
When it comes to exports to Russia, the picture is quite similar as for imports. Most of the Nordic countries had exports to Russia accounting for between 0 and 2% of the total value of exports between 2001 and 2021. Finland had a higher level during the whole period, between 5 and 12%, but the big exception here is Faroe Islands. In the beginning of the reported period, their exports to Russia were low, varying between 0 and 4%. In 2011, it started to increase and in 2017 it peaked at 29%. It then remained at levels around 23% before it dropped to 8% in 2022.
Most exports from Faroe Islands, averaging 86%, are exports of fish. And during its peak, up to 29% of those fish exports went to Russia. [2] There is a bilateral fishery agreement in place between the countries, but the future of this is unclear. [3]
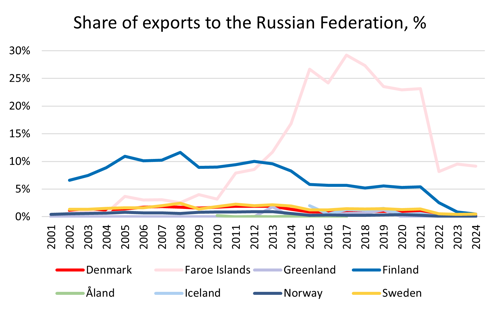
Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
Trade with the US
When it comes to trade with the US, the future is unknown. The annual numbers are not yet affected by the trade tariffs (possibly) being implemented. But to understand how big of a problem the Nordic region potentially is facing, it is important to know where we stand today.
The shares of trade with the US are, at a first glance, more volatile than those with for example Russia. Shares of import from the US varies between 3 and 8% of the total value of imports in the Nordic countries in 2024.

Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
The value of exports to the US accounts for between 3 and 13% of total exports in 2024.
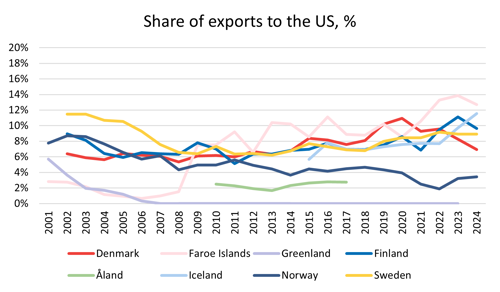
Source: Nordic Statistics Database, FOTR49
All countries report surpluses of trade with the US in 2024, except for Norway. They had a positive trade balance with the US for the first half of the reported period but have had a negative balance since 2014. Denmark, Finland, and Sweden had positive trade balances with the US the whole reported period, while Faroe Islands had a few years with a trade deficit between 2005 and 2008.
For Greenland and Åland, 2024 data is not yet available. Åland did however report surpluses for all years where data is available (2010-2017). Greenland reported a negative trade balance with the US in 2023 and have so for most of the years in the reported period.
_______________________________________________________________________
[1] 2023 values for Greenland and Åland as 2024 values are not yet available. Åland is included in the data for Finland.
[2] Hagstova Føroya: https://statbank.hagstova.fo/pxweb/en/H2/H2__UH__UH01/uh_sitc.px/
[3] More on the Faroese trade with Russia here: https://www.gransking.fo/en/resources/news/economic-ties-between-russia-and-faroe-islands-diminished-considerably